In the realm of modern timepieces, titanium watches have gained significant popularity.
Titanium, a material discovered in the 18th century in England, possesses a lustrous silver appearance and remarkable characteristics, including high strength, lightweight nature, excellent corrosion resistance, temperature endurance, and resistance to strong acids and alkalis.
With a density half that of stainless steel, titanium offers superior strength retention and far surpasses other metals in environmental corrosion resistance. Despite not being a rare metal, titanium ranks ninth in abundance among metallic elements in the Earth’s crust.
Due to its exceptional attributes, titanium finds extensive application in aerospace, automotive, military, industrial, medical, outdoor, and even jewelry industries. Watchmaking is no exception to the utilization of titanium as a valuable material.

The supply of titanium ore can last for at least ten thousand years. Its presence has been discovered in meteorites, lunar rocks, the sun, and other celestial bodies.
However, the extraction process of titanium is relatively slow and costly, which contributes to its expensive price. For many years, the high cost of titanium has limited its use in the military and aerospace sectors.
In the field of watchmaking, titanium offers several advantages over stainless steel, including its lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. White metal watches, including those made from titanium and platinum, are highly sought after.
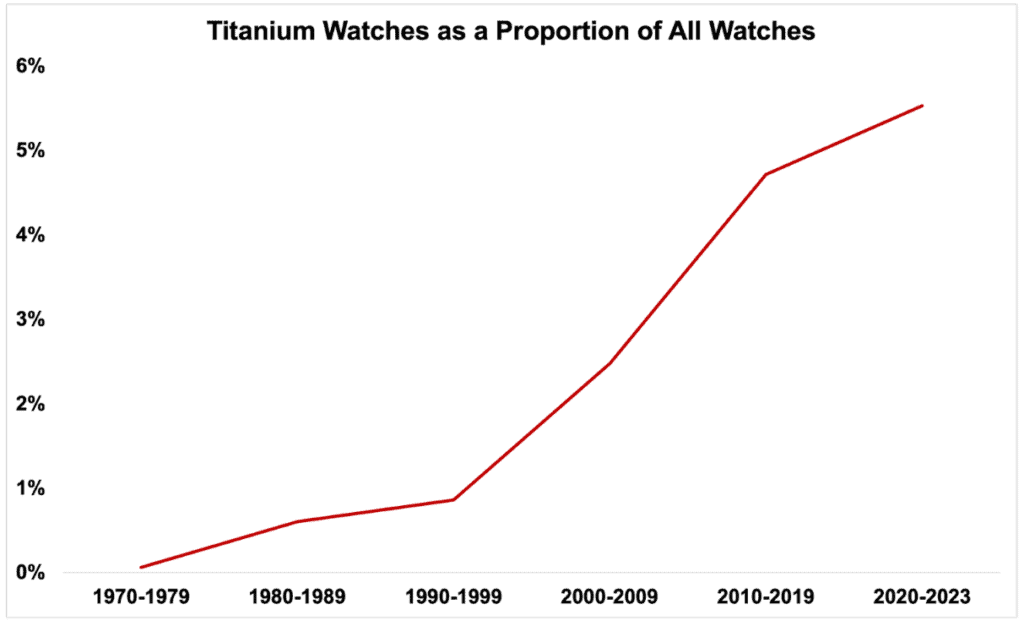
While the number of titanium watches may not surpass those made from stainless steel, the prevalence of titanium timepieces has increased significantly in recent years.
The benefits of Titanium watches:
Lightweight
Titanium possess a remarkable feature – they are approximately 40% lighter than stainless steel. This characteristic translates into enhanced comfort, especially for those who wear their watches for extended periods.
Sturdy:
Despite their lightweight nature, titanium are incredibly sturdy. They surpass stainless steel in terms of resistance to cutting, processing, and bending. This exceptional strength allows titanium watches to endure various challenges, including impacts and falls, making them exceptionally durable timepieces.
Corrosion Resistance:
One of the outstanding properties of titanium is their exceptional resistance to corrosion. Whether exposed to seawater, sweat, or other corrosive liquids, titanium watches remain unaffected, ensuring they maintain their integrity even during water-based activities such as diving and other water sports.
Unique Appearance:
Titanium watches boast a distinctive and captivating appearance. The surface of titanium can undergo various treatments such as polishing and brushing, creating a range of visual effects. Additionally, the unique colors of titanium, often silver-gray or black, contribute to the overall appeal of these timepieces.
Compared to stainless steel, titanium possesses a lower weight and density. For instance, Grade 5 titanium, also known as Ti-6Al-4V, can achieve a strength of 1000 MPa, which is five times that of stainless steel. The density of titanium is approximately 4.5 g/cm³, while stainless steel has a density of 8 g/cm³.

Today, the popularity of titanium watches is on the rise, with a more detailed categorization of titanium alloys. After refinement, titanium can be alloyed with other metals or elements.
According to the standards set by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), titanium can be classified into 38 grades. The most commonly used grades in watchmaking are Grade 2 and Grade 5 titanium.
Grade 2 titanium exhibits characteristics such as lightweight and corrosion resistance, while Grade 5 titanium offers even higher strength (containing 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium) but is relatively more challenging to manufacture, resulting in higher prices for watches crafted from this grade.
Some Titanium Watches From Renowned Brands
Let’s take a closer look at some renowned brands and explore the types of titanium they utilize in their timepieces.

As an example from 2022, some models in the Bulgari Octo Finissimo series are crafted from Grade 5 titanium. This alloy composition includes 6% aluminum, 4% vanadium, 0.25% iron, 0.2% oxygen, among others. Not only does it possess high strength, but it also exhibits a refined luster, creating an approachable appeal. Grade 5 titanium is widely used in bezels of titanium watches.
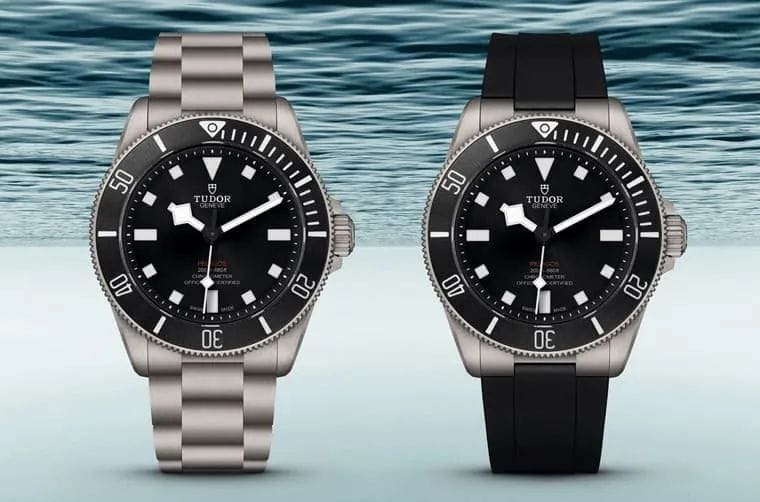

On the other hand, the Tudor Pelagos 39 features a case made of Grade 2 titanium, which belongs to the category of “commercially pure titanium.” It exhibits excellent oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, and moderate strength.
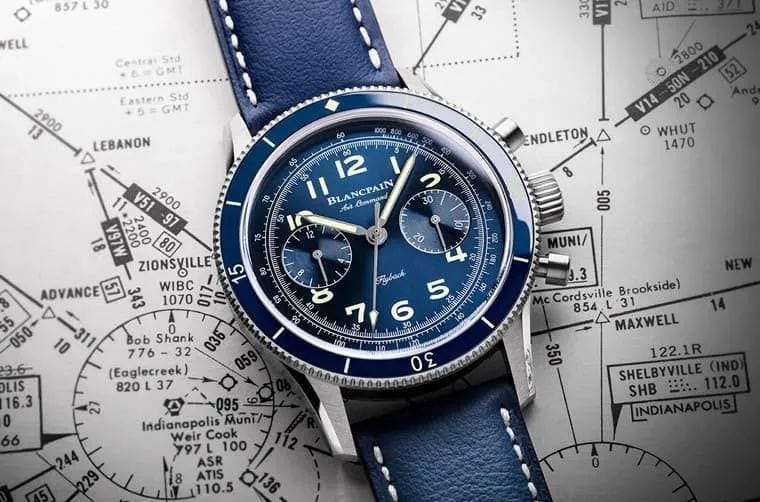

Blancpain Air Command Flyback Chronograph with a rare Grade 23 titanium case. Occasionally, we come across the use of Grade 23 titanium, such as in the Blancpain Air Command and Fifty Fathoms Bathyscaphe series.
This grade of titanium is free from iron and contains up to 0.13% oxygen. Due to its biologically inert properties, it finds applications in the medical field as well. It is safe to assume that timepieces crafted from this grade offer exceptional skin compatibility. However, due to the rarity of watches made from this type of titanium, watchmakers tend to use it less frequently.

Brands like CITIZEN and German brand SINN focus on developing titanium coatings to enhance the material’s hardness and scratch resistance. CITIZEN employs the TEGIMENT technology, while SINN introduces the Super Titanium™ material, which utilizes the Duratect process to increase the Vickers hardness of titanium to over 1000, making it three to five times harder than Grade 2 and Grade 5 titanium.
Conclusion
The world of titanium in watchmaking encompasses a mesmerizing fusion of beauty, strength, and exquisite craftsmanship. From aerospace to medical applications, the allure of titanium continues to captivate watch enthusiasts worldwide.
[…] choose to use aerospace-grade titanium, Grade 5 to be exact, to make a watch band that is both strong and light. In fact, this titanium is […]
[…] choose to use aerospace-grade titanium, Grade 5 to be exact, to make a watch band that is both strong and light. In fact, this titanium is […]